Highly selective for CLK, CTX-712 is an orally available, first-in-class pan-CLK inhibitor.
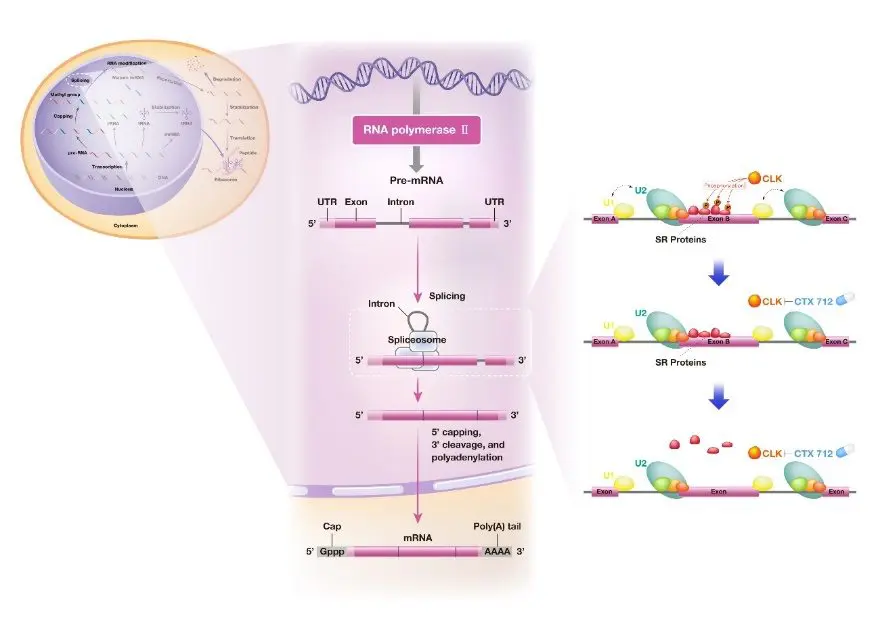
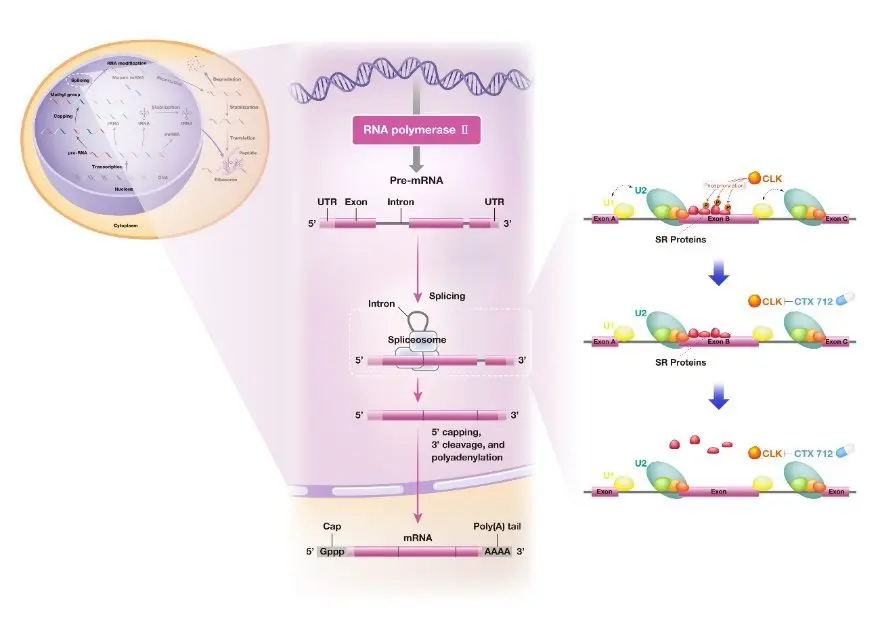
CTX-712 inhibits phosphorylation of serine/arginine-rich (SR) proteins by its target, CLK kinase, and induces accumulation of aberrant RNA primarily by inducing skipped exon type splicing abnormalities, which may generate excessive RNA deregulation stress.
To date, in several preclinical models, we have confirmed that it can induce cancer cell death in vitro, and induce anti-tumor effects in vivo.
CLK kinase phosphorylates the substrate SR protein.
SR proteins phosphorylated by CLK, as RNA splicing molecules, facilitate the recognition of specific exons in splicing.
CLK is composed of four family members: CLK1, CLK2, CLK3, and CLK4.
SR proteins are composed of an RNA recognition domain and an SR domain required for protein-protein interactions during splicing.
Several groups of protein phosphatases, including CLK, are known to phosphorylate SR proteins, and phosphorylated SR proteins promote normal splicing.
Splicing, a critical step in gene expression, is part of the RNA maturation process in which non-coding sequences (introns) are removed and then coding sequences (exons) are ligated together.
Splicing is catalyzed by the spliceosome, which is composed of multiple splicing factors.